DNS is to make your life easier by resolving your requested host or domain name to IP address when you browse via web browser, such as IE7 or Firefox. For example, you browse google.com, it will bring you to local google web page. You don't need to remember or key in the long and hard to remember IP address, in this case, google.com web site IP addresses are 64.233.187.99, 72.14.207.99 and 64.233.167.99. If you key in either of them into your web browser, it serves the same purpose. And these service is normally provided by your local ISP, such as TM Net, Singtel and AOL.
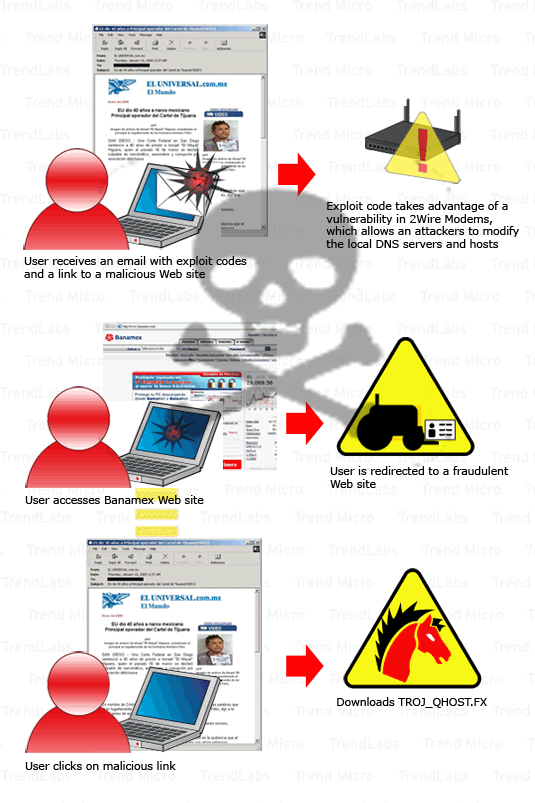
Process of one of the DNS vulnerability cases.
Since DNS is almost used by every Internet users, here's why the attackers came in for this. DNS Cache poison is the worst case among DNS vulnerabilities, although it is not a new concept. An attacker with the ability to conduct a successful cache poisoning attack can possibily lead you to contact the incorrect or malicious hosts for particular services. For example, you access certain web sites under cache poisoning DNS. Consequently, web traffic, email, and other important network data can be redirected to systems under the attacker's control.

DnsStuff.com is a very good and informative web site, but no longer free now.
So are you interested to know whether your country ISP Domain Name Service (DNS) is safe to use? Fine, just visit Dnsstuff and check it immediately.

If you are scare, just setup your own DNS so you can take control of it.
Good luck to you first!






No comments:
Post a Comment